BEST HAIR TREATMENT IN Kanpur, INDIA FOR HAIR LOSS, HAIR FALL IN MEN, WOMEN
Hair Loss and 'Difficult To Manage' Hair
Hair has always acquired a great deal of social and cultural importance. Hair loss, a condition also known as alopecia, generally refers to the loss of hair from any part of the hair bearing area of the body, like the scalp, eyebrows, beard or all over the body.
WHAT ARE TYPES OF HAIR LOSS?
Normal hair growth cycles last anywhere from 2-7 years. However, forms of hair loss are characterized by shorter hair growth cycles such as in androgenic alopecia.
A normal human growth cycle consists of 3 phases as:
- Anagen phase (main growing stage).
- Catagen phase (resting stage).
- Telogen phase (shedding off stage).
When telogen phase ends, old hair gets replaced with a new hair from the same follicle. Normally a person sheds about 50-100 hair strands per day, but it is not noticeable. However, with the gradual increase in thinning of hair, hair loss becomes prominent.
CERTAIN FACTORS ARE INVOLVED IN THINNING OF HAIR, WHICH INCLUDE:
- The most common form of male hair loss is androgenic alopecia, also called male pattern balding. This is an inheritable form of balding that comes with aging and is mediated by the active form of the hormone testosterone called DHT.
- Similar condition in females is called Female Androgenetic alopecia due to a multitude of hormone disturbances, which could also be heritable.
- Telogen effluvium is another type of hair loss which is usually temporary that is as a result of the effect of stress on the body. This stress may be caused by illness, pregnancy and childbirth or weight loss and nutritional deficiency etc.
- Patchy hair loss also termed alopecia areata, which occurs suddenly on any part of the body where hair grows.
- Trichotillomania, due to pulling of hair deliberately; this is a psychological disorder.
- Certain drugs like anti cancer medication, radiation therapy can cause hair fall.
- Scarring alopecia occurs due to skin diseases like lichen planus, lupus etc. and they are irreversible.
The specific type of hair loss can be determined by common blood and hormone investigations. A biopsy of the scalp may also be done to confirm the type of alopecia in some cases.
WHAT ARE THE HAIR TREATMENTS AVAILABLE?
- Medications can be administered to prevent further hair loss for example minoxidil, Finasteride, flutamide etc. depending on the cause of the hair fall.
- Hair supplements in case of nutritional deficiency
- Hormone correction if required, for example in cases associated with polycystic ovarian syndrome.
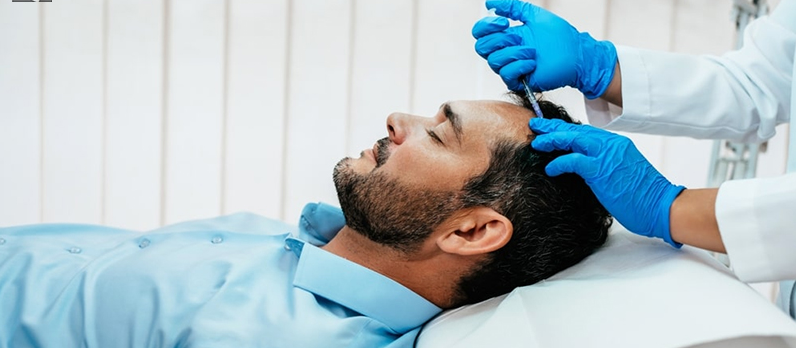
- Platelet rich plasma injections
- Stem Cell Treatment: Stem cells taken from your own fat or peripheral blood , referred to as Autologous stem cells, are injected into the affected area These cells release factors which send molecular signals to hair follicles which are revivable, which then give rise to new hair growth.
- Hair transplant: For later stages wherein hair re-growth with medical means is no longer possible, Follicular unit transplant, follicular unit extraction, or the latest direct hair implant techniques can be used.
- Studies are underway for genetic remodelling for Androgenetic alopecia, generation of hair follicle with stem cells in the laboratory, hair cloning etc. However, they are still in the initial stages and will take years before they can be used in humans.
- Laser treatment can also be done as adjunct though the results are unproven in clinical studies.
Book Online Appointment
About Doctor

Experience the full spectrum of result-oriented whitening treatments tailored to your individual body and social preferences, administered by the top Skin and Hair Doctor in Kanpur. Our approach is both safe and cost-effective. Begin your journey with a skin test to determine the most suitable treatment for you.
ARE ANY OF THE TREATMENTS PERMANENT?
All treatments including transplants come with a shelf life especially in Androgenetic alopecia and maintenance is the norm.
WHAT ARE DIFFERENT STRATEGIES TO PREVENT HAIR LOSS?
Hair loss can be prevented by:
- Healthy eating habits
- Iron and protein rich diet
- Regular exercise
- Avoiding medications and chemicals that are likely to cause hair loss
- Stress management.
- Using the right products on the hair and limited hair styling treatments.
What must one remember while undergoing this treatment?
- Every skin is different, just like every individual is unique. One must have realistic expectations and not get carried away by advertisements, results obtained in other patients, celebrities etc.
- A trained expert cosmetic dermatologist with ample years of experience should be your treating physician.
- There may be cases in which nothing works. This is sad but true as there are still some gaps in our knowledge in this subject.